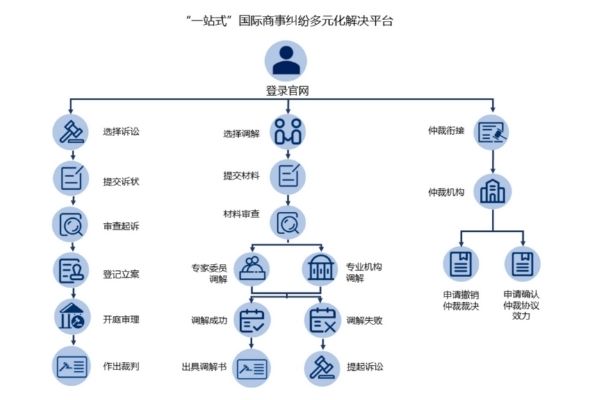
On 21 July 2021, China’s Supreme People’s Court (SPC) launched its “one-stop” diversified international commercial dispute resolution platform (hereinafter referred to as “the Platform”) on the official website of China International Commercial Court (CICC).
Three years ago, the SPC set up the First/Second International Commercial Court respectively in Shenzhen and in Xi 'an on 29 June 2018, along with the International Commercial Expert Committee, providing a “one-stop” diversified international commercial dispute resolution mechanism that integrates litigation, mediation, and arbitration.
Nowadays, in order to meet the needs of parties involved in online dispute resolution in the Internet era, the SPC builds the online “one-stop” diversified international commercial dispute resolution platform, enabling both Chinese and foreign parties to participate in the whole process of dispute resolution online, such as case filing, mediation, evidence exchange, and court trials.
The platform provides both Chinese and English versions to facilitate foreign parties to understand and use various functions of the Platform. The Platform also integrates the functions of the SPC’s unified Foreign Law Ascertainment Platform to facilitate the ascertainment of foreign laws.
The parties can log into the Platform either through the official website of CICC or the WeChat applet, "China Mobile Mini Court" on cellphones.
(Photo from http://cicc.court.gov.cn/html/1/218/149/192/2084.html)
Cover Photo by 再一 王 (https://unsplash.com/@gary9777) on Unsplash
Contributors: CJO Staff Contributors Team









