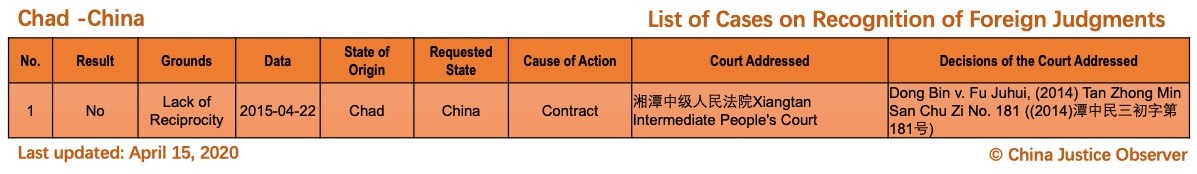
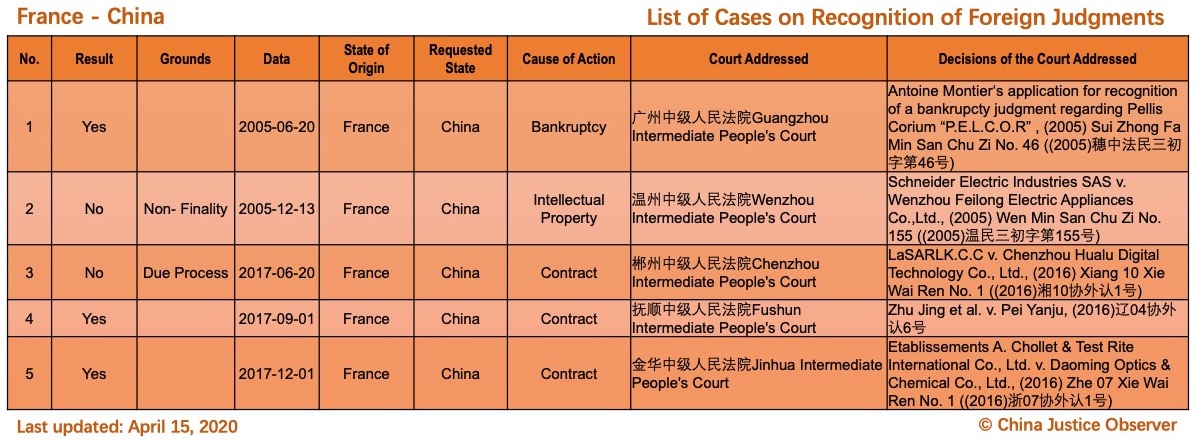
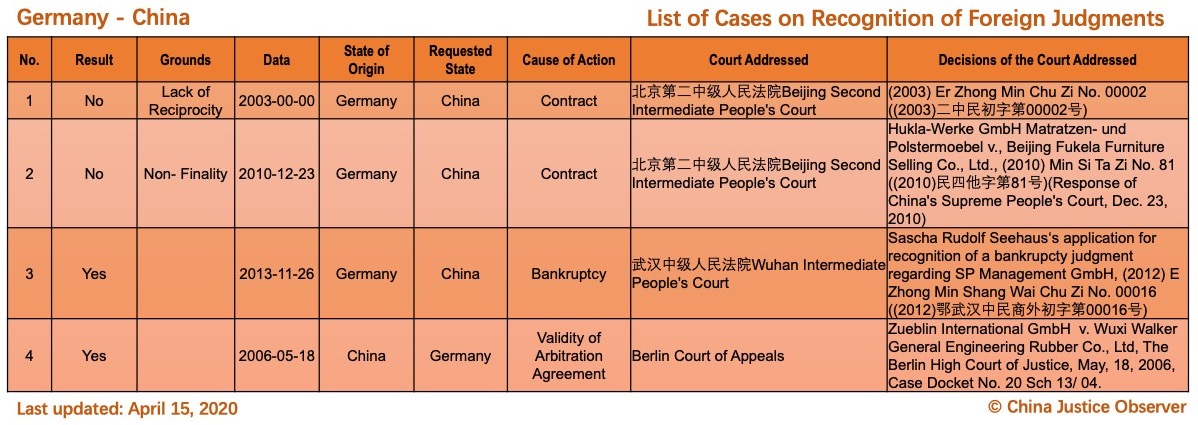
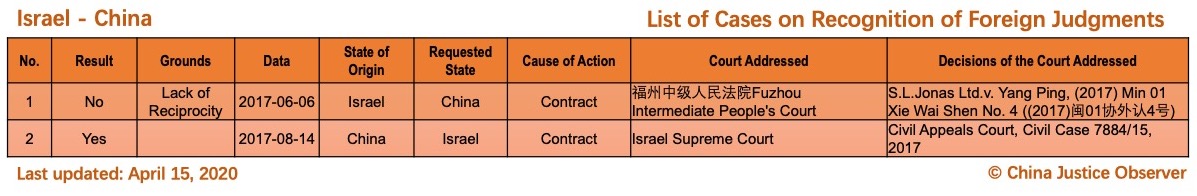
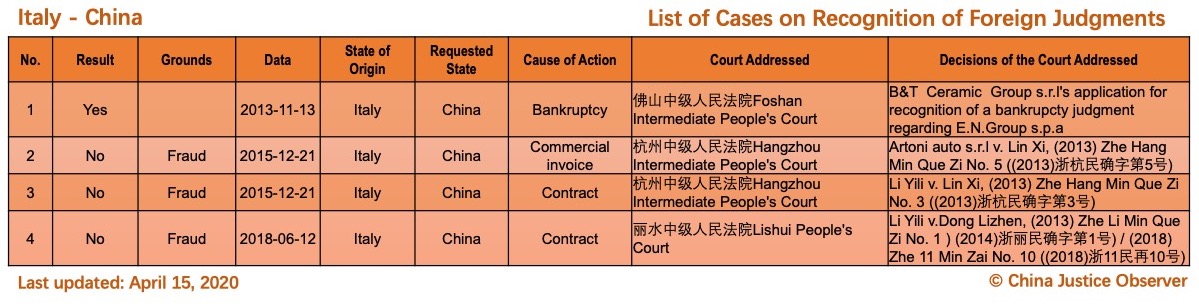
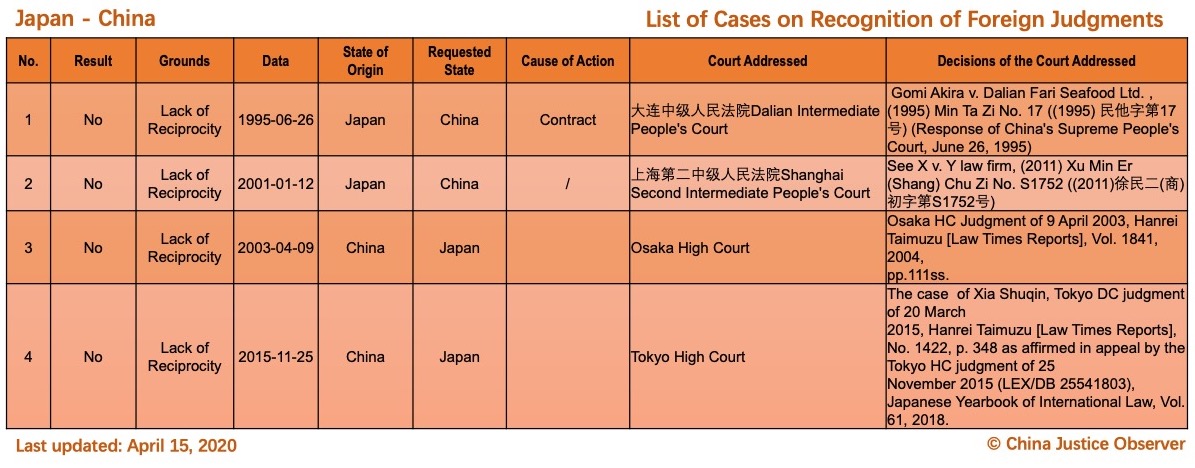
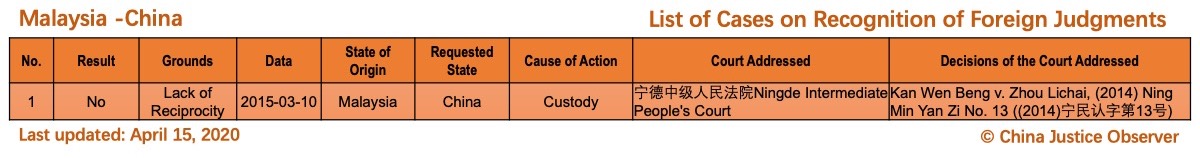
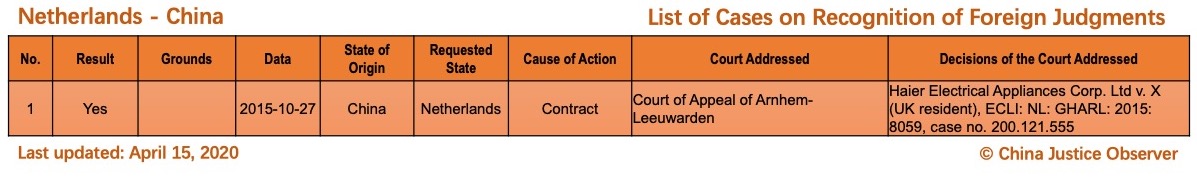
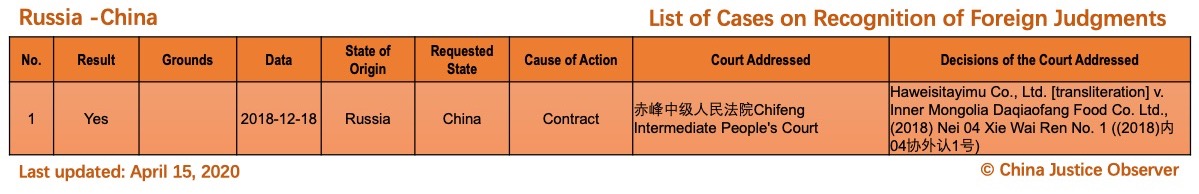
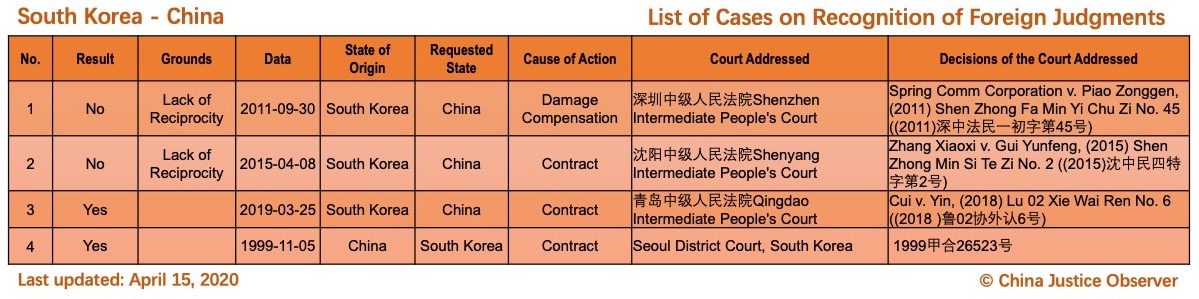
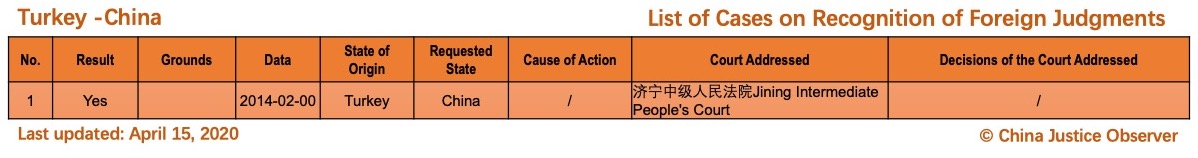
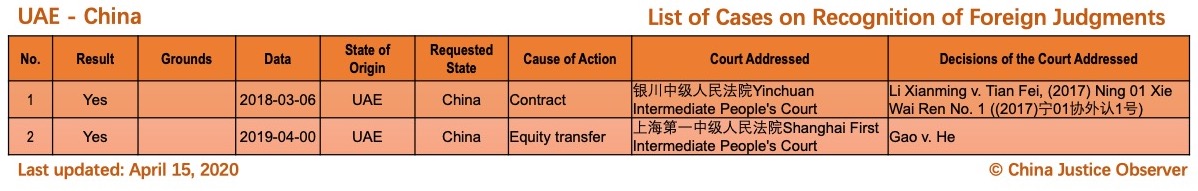
On 15 April 2020, China Justice Observer released the 2020 version of List of China’s Cases on Recognition of Foreign Judgments. To date, we have collected 57 cases involving China and 20 foreign States and regions. (Note: Foreign divorce judgments are excluded in the Case List.)
You can download the Case List here.
(For the List of China's Bilateral Treaties on Judicial Assistance in Civil and Commercial Matters (Enforcement of Foreign Judgments Included), please click here. Authoritative texts in Chinese and other languages are now available. )
The key features of the updated list are:
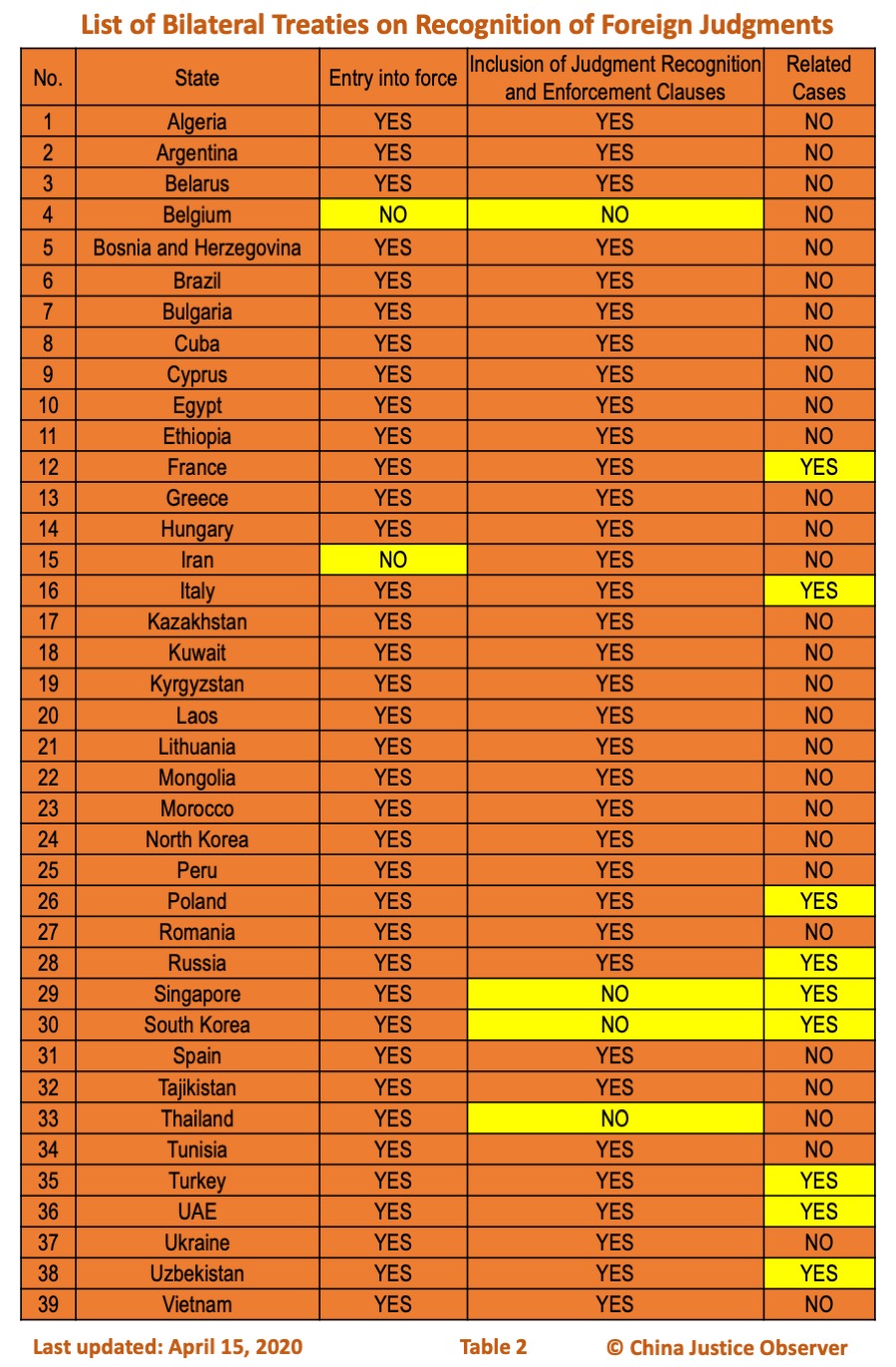
- The List comprises 20 concise reports for each jurisdiction, together with a chart for bilateral judicial assistance treaties that China and 39 States have concluded, among which 35 bilateral treaties include the judgment enforcement clauses.
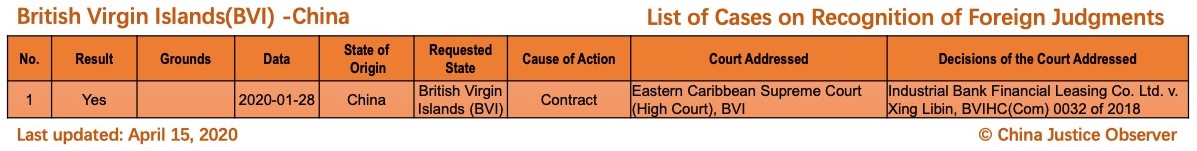
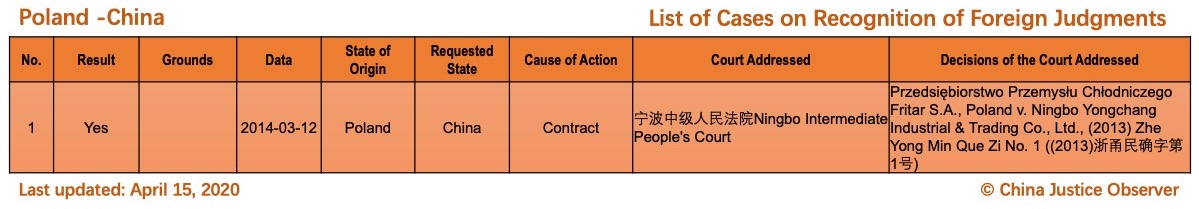
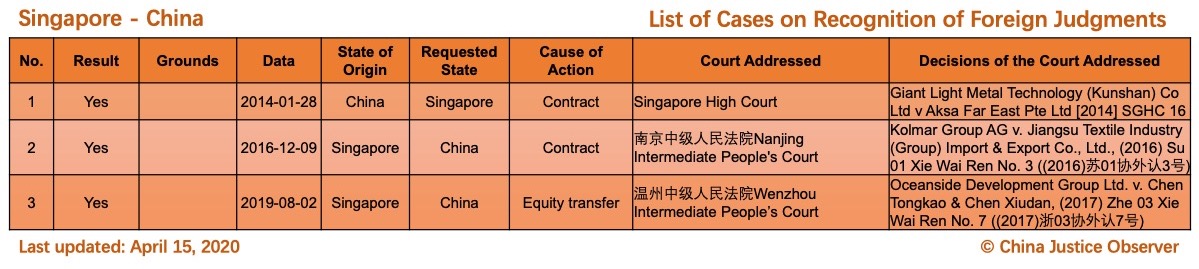
- First time the cases involving 3 jurisdictions (i.e. Netherlands, Uzbekistan, British Virgin Islands) are included.
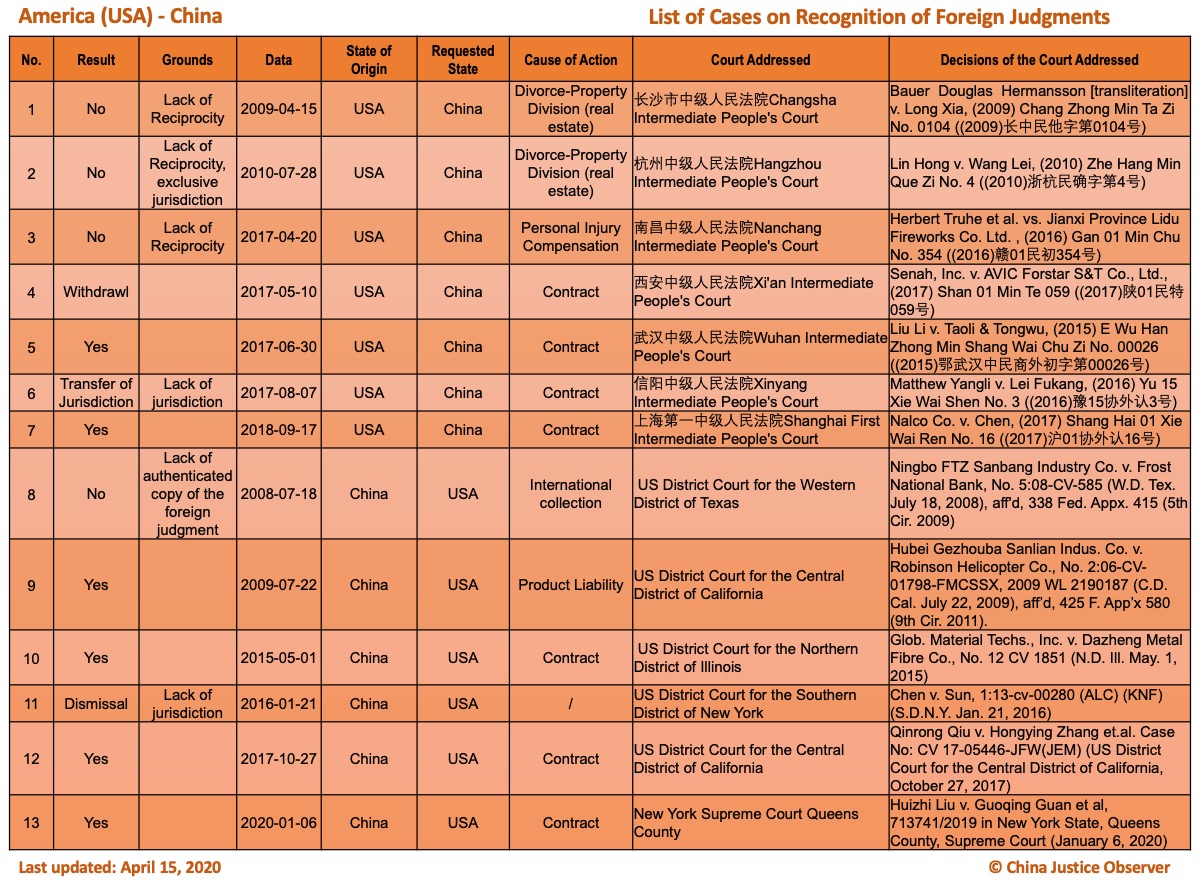
Please note that there are two landmark cases where Chinese judgments are recognized for the first time in the Netherlands and in the British Virgin Islands respectively. The Dutch case (Haier Electrical Appliances Corp. Ltd v. X) is discussed in a recent article by Dr. Yahan Wang. - 6 cases involving the existing two jurisdictions, namely, the U.S. (five cases) and Singapore (one case) are added. Please note that the case of Huizhi Liu in 2020 (potentially) marks the fourth Chinese judgment recognized in the U.S. and the first in New York,and the case of Oceanside Development Group Ltd. in 2019, being the second Singapore judgment recognized in China, marks the first time that a Singapore judgment has been recognized in China since the signing of China-Singapore Memorandum of Guidance in 2018.
- Each case has been reviewed, and more details, such as the case numbers, are added.
As always, we endeavor to collect all Chinese court decisions involving the recognition and enforcement of foreign judgments (“REFJ”), and foreign counterparts concerning the recognition and enforcement of Chinese judgments. The Case List is made available for our readers to build reasonable expectations on REFJ in China.
The Case List is continually updated with new reports. Case information, comments, and suggestions are most welcome. Please feel free to contact Ms. Meng YU via e-mail at meng.yu@chinajusticeobserver.com.
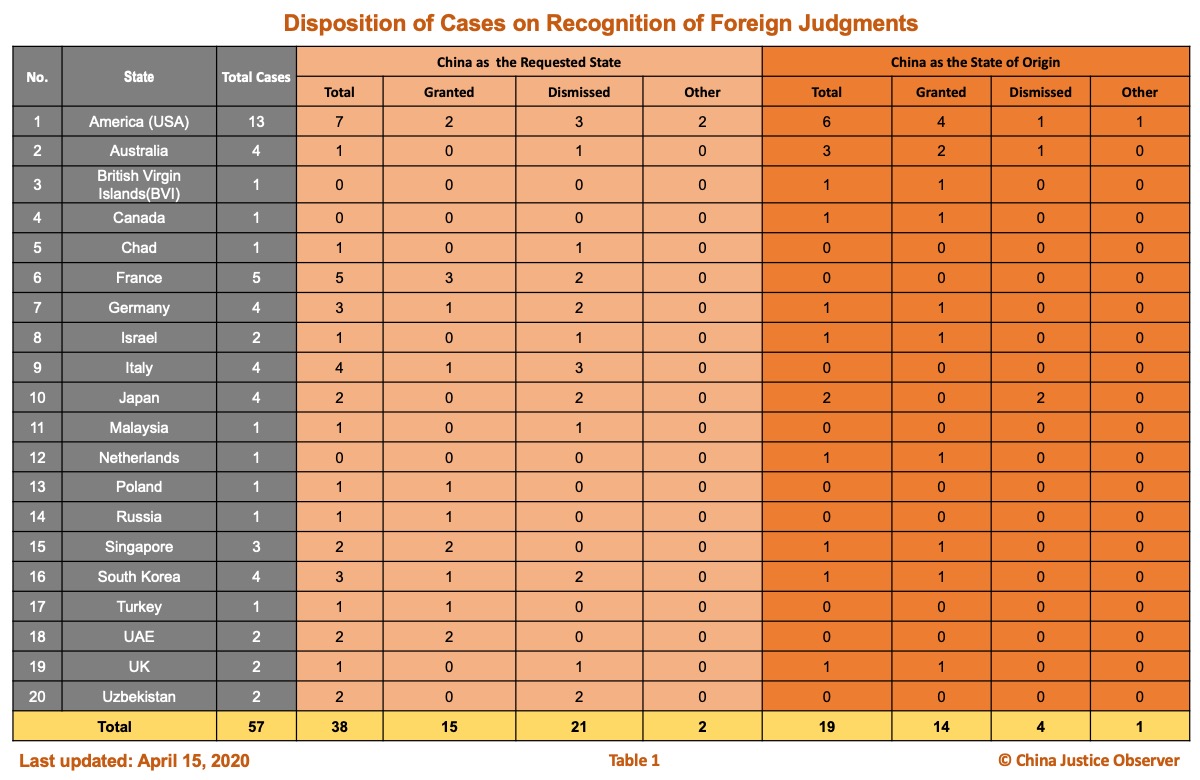
For an overview of the disposition of cases on REFJ, please see table 1 below.
For information about bilateral judicial assistance treaties that China and 39 States have concluded, please see table 2 below.
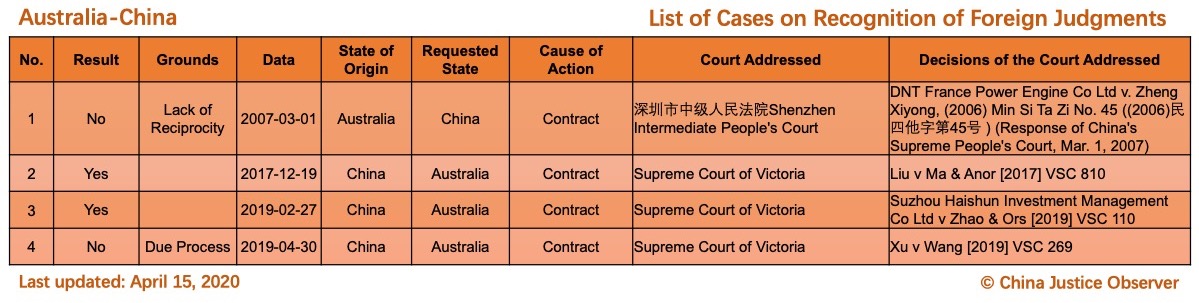
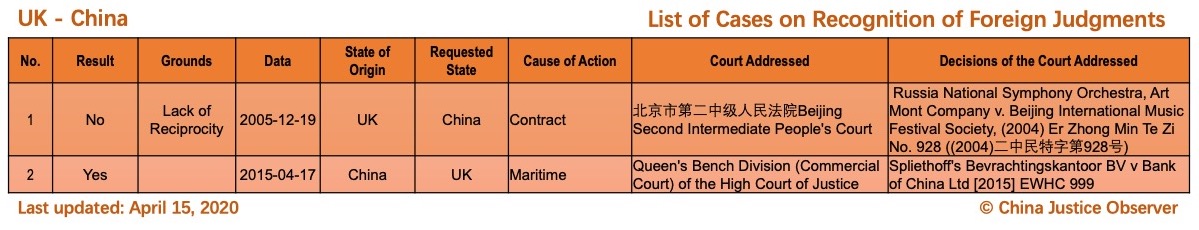
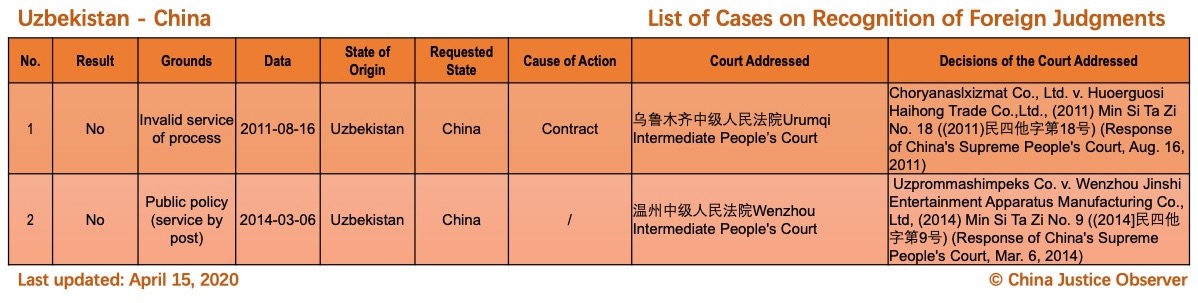
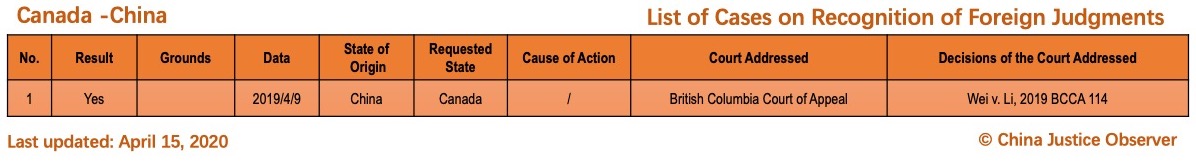
For the detailed country(region) report about cases on REFJ, please see the following charts.
Cover Photo by 五玄土 ORIENTO(https://unsplash.com/@oriento) on Unsplash
Contributors: Guodong Du 杜国栋 , Meng Yu 余萌